EN 1090
The EN 1090 standards are European standards that regulate the fabrication and assembly of steel and aluminium structures and are recognized by the Construction Products Directive (CPD).
EN 1090 comprises three parts:
EN 1090-1: Requirements for conformity assessment for structural components.
EN 1090-2: Technical requirements for the execution of steel structures.
EN 1090-3: Technical requirements for the execution of aluminium structures.
A company can be certified according to EN 1090-1..

As of July 1st 2014 any manufactured structural metal components and to which a harmonised European standard applies must comply with the CPD and get CE marking. The standard that applies to structural metalwork is EN 1090-1 and when mandatory it will be a criminal offence to supply products not conforming it.
See
Clarification on CE marking with EN 1090-1
ISO EN 3834
The objetive of EN ISO 3834 is to demonstrate the capabilities of the manufacturer to control welding activities for the type of work being done. Welding is a special process that cannot be completely verified without destroying the product so it is recommended to implement special measures into the Quality Management System (QMS) to ensure proper quality of the production.
The main parts of the standard are the following:
- ISO 3834-1, Quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials - Part 1: Criteria for the selection of the appropriate level of quality requirements
- ISO 3834-2, Quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials - Part 2: Comprehensive quality requirements
- ISO 3834-3, Quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials - Part 3: Standard quality requirements
- ISO 3834-4, Quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials - Part 4: Elementary quality requirements

Although a company can be certified according to EN ISO 3834, it does not specify requirements for a total quality management system (QMS), it must be used in conjunction with EN ISO 9001 to get a full QMS which includes the specific requirements from welding.
ISO 9001
ISO 9001 is a well-known and most recognised standard which specifies requirements for a Quality Management System (QMS) where an organization needs to demonstrate its ability to consistently provide product that meets customer and applicable statutory and regulatory requirements.
It focuses on continual improvement and customer satisfaction.
All requirements of ISO 9001 are generic hence it can be implemented to all organizations, regardless of type, size and product provided.

A new version of ISO9001 is to be released during 2015.
WELDING

Welding is a technology in a constant development pushed by manufacturing issues and the use of new materials. New techniques are developed and the existing ones are improved. For such reason it is highly recommended a continuous training on the subject.
The technological developments in this field are a consequence of the study and understanding of the physical transformations which happen during welding. All this knowledge has brought a new science branch called welding metalurgy which is becoming essential to work with metals and their alloys.
There are numerous standards which cover a wide range of welding disciplines and areas including procedures, welder qualification, welding equipment, consumables, coordination and much more.
NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
Non Destructive Testing (NDT) is a wide group of analysis techniques used in industry to evaluate the properties of a material or component without permanently altering the physical, chemical, mechanical or dimensional characteristics of the object.
The fact that these testing techniques don´t damage the material allow to check 100% of the production ensuring quality and reliability of the product. Moreover the NDT are very useful to check pieces already in service preventing fatigue failures.

Common NDT methods include radiographic, ultrasonic, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, visual inspection and eddy-current testing.
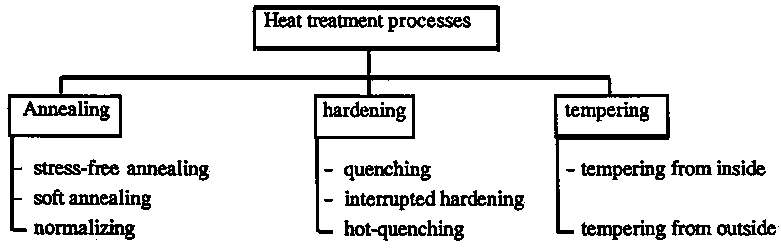
HEAT TREATING

Heat treating is a group of processes which are applied to metals and their alloys to change the physical properties of a material. Those processes make use of heating and cooling at controlled temperatures and speeds to cause metallurgical changes within its structure. The properties which can be altered are toughness, shear strength, tensile strength and hardness.
The most common heat treatments are: